Lapsus$ is an international hacking group known for conducting cyberattacks against various companies and government agencies. The group gained notoriety for its extortion-focused activities and has targeted organizations globally.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the Lapsus$ extortion group techniques, how the attack happens, and what to do if Lapsus$ compromises your systems or machines. Also, see how you can protect your business’s sensitive and critical data by taking simple preventive actions.
Lapsus$ extortion group overview
Lapsus$ is associated with cybercrimes such as ransomware attacks, data breaches, and extortion attempts.
The group employs a variety of attack vectors, including social engineering, SIM swapping, and targeting suppliers. Once they gain access to a target organization, Lapsus$ attempts to obtain sensitive data through remote desktop tools.
Lapsus$ communicates with the public, recruits members, and posts sensitive data from victims through messaging platforms like Telegram. This is not a RaaS (Ransomware as a Service), which is a model of businesses where developers sell their ransomware tools. Lapsus$ actually brings people into their group as “employees”.
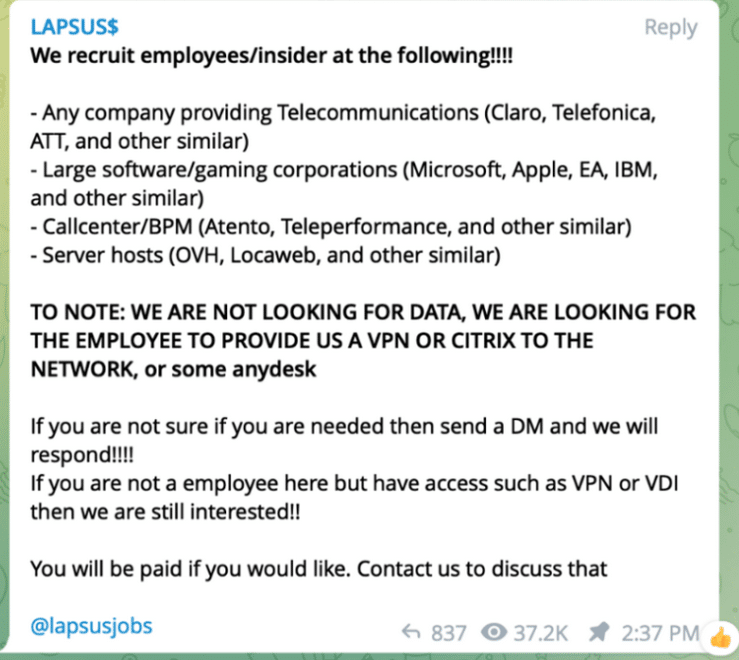
The group’s activities have led to arrests in various countries, including Brazil and the UK. Despite facing legal actions, Lapsus$ has demonstrated resilience and has been associated with multiple instances of re-emergence after periods of inactivity.
The group’s tactics include not only traditional ransomware (data encryption and ransom demands) but also threats of exposing stolen data to coerce payments from their victims. This tactic is known as double extortion.
How to identify Lapsus$ ransomware: Main IOCs
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) are pieces of forensic data that can help identify malicious activity or malware associated with a cyber attack. It includes the encryption extension, file hashes, and IP addresses, among other details cyber criminals leave as they infect a machine or system.
But, if you can’t identify the ransomware strain through its IOCs, you can use Proven Data’s free ransomware ID tool to check if the Lapsus$ ransomware is the malware that encrypts your files.
Important: Some of these indicators require technical knowledge of the infected system, so you may need to contact your IT team or a digital forensics service provider.
It’s important to note that Lapsus$ is not typically associated with traditional ransomware attacks that involve encrypting files on a victim’s system. Instead, Lapsus$ is known for its extortion-focused approach, where the group threatens to expose sensitive data unless a ransom is paid.
Lapsus$ IOCs include:
- Encrypted Files Extension: .locked
- URL: http://8.3.1.0
- IP address: 104.238.222[.]158
- IP address: 108.61.173[.]214
- IP address: 185.169.255[.]74
- Domain: hxxps://filetransfer[.]io
- FileHash-SHA256: 2f578cb0d97498b3482876c2f356035e3365e2c492e10513ff4e4159eebc44b8
- FileHash-SHA256: 065077fa74c211adf9563f00e57b5daf9594e72cea15b1c470d41b756c3b87e1
- FileHash-SHA1: f9153289b209929130f897ee47710b4c94aa6453
- FileHash-SHA1: 91b88d281ef983296157f8ebfc73958036148194
- FileHash-MD5: 61089a51d3be666631053d516ad9b827
How Lapsus$ ransomware works
As with most ransomware, Lapsus$ uses several techniques to infect a machine or network, evade detection, exfiltrate data, and then encrypt files.
1. Initial Access
Lapsus$ initiates its attacks through diverse methods, primarily on obtaining stolen authentication cookies, often sourced from Single Sign-On (SSO) applications.
These pilfered cookies serve as a gateway, granting the threat actors access to specific applications and enabling them to pivot into other critical corporate systems.
Central to Lapsus$’s strategy is the acquisition of access to corporate VPNs. The group employs a tactic where compromised employee email accounts are utilized to interact with helpdesk systems. Through this interaction, Lapsus$ seeks to obtain access credentials or support, facilitating their entry into the corporate VPN, which is crucial for furthering their objectives within the targeted infrastructure.
2. Credential Access and Privilege Escalation
The strategic combination of credential harvesting and rapid escalation of privileges within the compromised environment is critical to Lapsus$ operations. The group achieves this without heavy reliance on traditional malware, often opting for legitimate tools like Sysinternals’ ADExplorer for reconnaissance purposes.
The result is a swift transition from standard user accounts to administrative user accounts, typically accomplished within a short time frame of just a couple of days.
3. Lateral Movement
Lapsus$ executes lateral movement within the victim’s environment, employing techniques such as sporadic use of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to navigate deeper into the network.
Observations of disclosed victim-controlled hostnames, such as “VULTR-GUEST,” indicate deliberate endeavors aimed at accessing resources hosted on private cloud services, thereby playing a role in the group’s comprehensive penetration strategy.
4. Exfiltration
The primary objective of Lapsus$ revolves around data exfiltration (unauthorized transfer of data from a computer or network to an external location), with a particular focus on sensitive information.
Stolen data is freely transferred to external locations through external services. The group targets what they deem valuable assets, including application source code, proprietary technical information, and other critical data crucial to the targeted organizations.
5. Impact
The aftermath of Lapsus$ actions is marked by disruption and destruction within client environments.
Activities range from the strategic shutdown of virtual machines to the extreme measure of mass deletion of resources in on-premises VMware ESXi infrastructure and cloud environments.
The stolen data is concentrated on high-value assets, such as application source code, holding commercially sensitive intellectual property and API keys, intensifying the impact on the victimized organizations.
The group threatens to leak the stolen data unless the victims comply with their ransom demands.
Important: Do not pay the ransom. Paying the ransom does not guarantee that you will get your data back, and it may encourage the attackers to continue their criminal activities. Check our in-depth article on what happens if you pay the ransom.
How to handle a Lapsus$ ransomware attack
It is important to note that handling a ransomware attack can be complex and requires expertise. Therefore, it is recommended to seek professional help from a reputable data recovery service, such as Proven Data to help you recover your data and remove the ransomware from your system.
You can also report the attack to law enforcement agencies, such as the FBI, and cybersecurity organizations to help prevent future attacks and catch the perpetrators.
We strongly recommend contacting cybersecurity services to handle ransomware attacks. Proven Data technicians not only retrieve ransomware-encrypted data but also create forensic reports and streamline incident response, minimizing your business downtime and financial loss.
Notable attacks by Lapsus$ ransomware
The Lapsus$ group is known for multiple attacks against the tech industry and governmental agencies. These are the three biggest attacks the group made in the last few years:
Brazil's Ministry of Health attack
In December 2021, Lapsus$ gained notoriety with its initial public appearance through a ransomware attack on Brazil’s Ministry of Health. The group compromised the COVID-19 vaccination data of millions within Brazil, marking its entrance into the cyber threat landscape.
Cyberattacks on tech companies
Lapsus$ escalated its activities in March 2022 by targeting major technology companies, including Nvidia, Microsoft, Okta, Samsung, and Vodafone. These attacks involved data theft and disruption of services, showcasing the group’s ability to compromise high-profile enterprises.
Ubisoft and EA Games
On several occasions, Lapsus$ demonstrated its impact on the gaming industry by disrupting the services of gaming companies such as Ubisoft and being suspected of involvement in the attack on EA Games. While user data was not compromised in Ubisoft’s case, the group’s actions underscore its reach across diverse sectors.
How to prevent ransomware attacks
Preventing Lapsus$ ransomware attacks is always the best cybersecurity tactic. If you are a recent victim, you must follow these tips to avoid a new ransomware attack:
Keep your software up to date
Regularly update your operating system and programs to uphold security standards. Reputable OS providers will consistently check their software for vulnerabilities and patch up their security standards to protect against newly detected threats.
Use reputable antivirus software
Employ reputable antivirus software to significantly bolster protection against malware, and regularly check that it is updated. You can also check your network for vulnerabilities and learn where you need to improve your security system.
Be cautious of suspicious emails
Even though there are no known cases of Lapsus$ using phishing as an attack method, it’s important to exercise caution when dealing with emails from unfamiliar or dubious origins. Refrain from opening files or clicking on links within emails that you are not expecting or that seem suspicious.
Do not download cracked software
Cracked software is the term used to describe illicitly modified or pirated versions of commercial software, typically distributed without proper authorization or licensing. Cybercriminals frequently conceal their ransomware executables within cracked software distribution websites, leading users to unwittingly download and execute the malware.
Backup your data
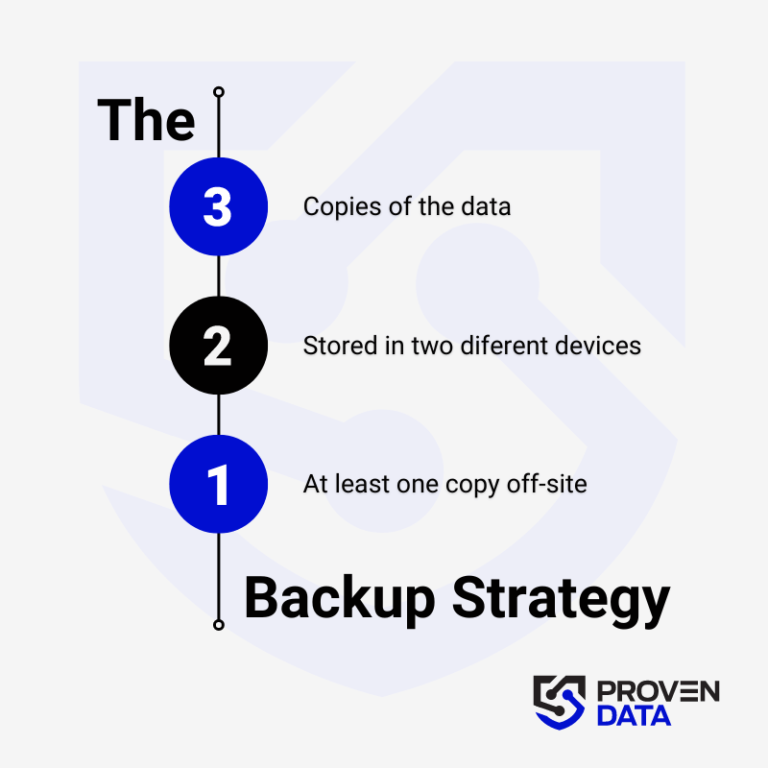
Regularly back up your data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service to prevent complete data loss in case of a ransomware attack. A highly recommended strategy for data loss prevention is the 3-2-1 backup strategy.
The 3-2-1 backup strategy involves creating three total copies of your data: two on different media and one offsite, ensuring redundancy and protection against data loss. And at least one copy offsite to prevent loss due to natural disasters or other local incidents.
Educate yourself and your teams
Educate yourself and your employees about the risks of ransomware and how to avoid it, such as avoiding suspicious emails or downloads.
Consult cybersecurity professionals
Proven Data offers cyber security services to help you keep your data protected against threat actors. From vulnerability assessment to ensure your systems and servers do not have open doors for cyber attacks, to Incident Response (IR) services for immediate response in case of a successful attack.
We also have the option of managed detection and response (MDR) services that help organizations improve their security posture, minimize risk, and protect sensitive data and assets.