Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats posed by security weaknesses in systems and software.
As cyber threats evolve and become more sophisticated daily, vulnerability management has become an essential component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It’s one of the most efficient ways to prevent cyber attacks, such as ransomware, and provide enhanced security to networks, systems, and stored data.
The importance of vulnerability management
Effective vulnerability management ensures that an organization’s systems remain secure and up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. Recent research reveals that nearly 95% of assets contain at least one highly exploitable vulnerability, highlighting the pervasive nature of vulnerabilities in modern IT environments and emphasizing why organizations must prioritize their identification and remediation.
Vulnerability management process
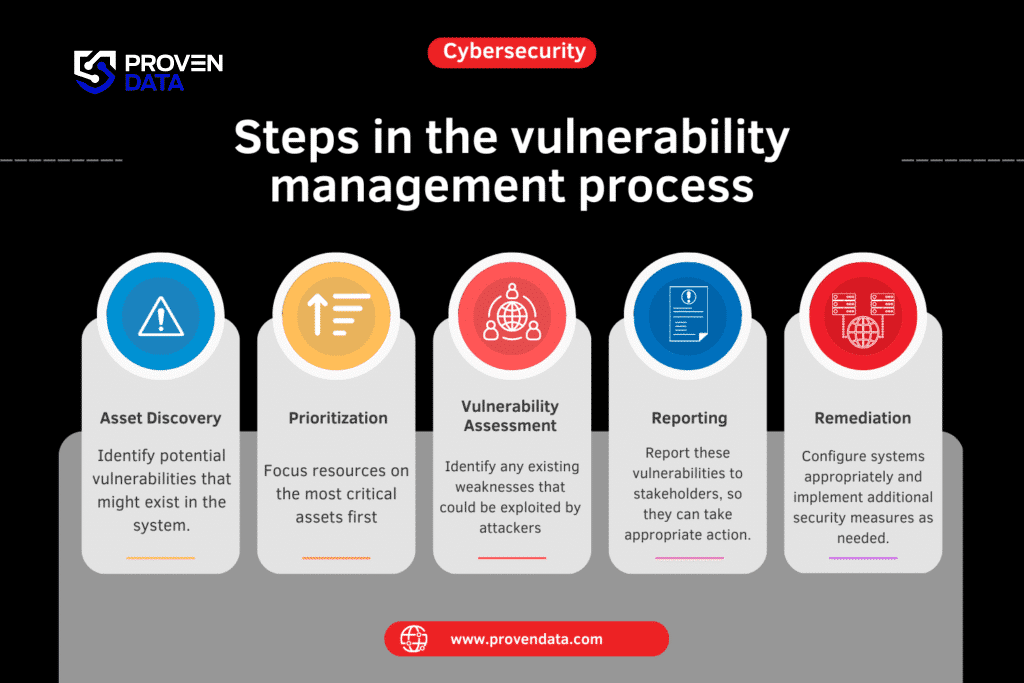
The vulnerability management process is an ongoing cycle that helps protect organizations from cyber threats by finding and remediating weaknesses in their IT infrastructure.
This process involves several activities, including scanning for potential vulnerabilities, assessing associated risks, and implementing measures to reduce or eliminate those risks.
Steps in the vulnerability management process:
1. Asset discovery
This initial step involves discovering all assets connected to the network and understanding their relationships. By creating a comprehensive inventory of all systems, devices, and applications, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities within their infrastructure.
2. Risk assessment and prioritization
After vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is to assess the risks associated with each vulnerability and prioritize them based on their severity and potential impact.
This is where the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) comes into play. CVSS provides a standardized method for rating the severity of vulnerabilities, with scores ranging from 0 to 10, where 10 represents the highest severity.
However, it’s important to note that modern vulnerability management goes beyond just CVSS scores. Risk-based prioritization has emerged as the gold standard, considering factors such as threat intelligence, asset criticality, and potential business impact. This approach helps organizations focus their limited resources on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first.
3. Vulnerability assessment
Once assets are identified, vulnerability assessment services providers conduct scans to discover vulnerabilities using automated tools or manual processes.
It’s important to note that vulnerability scanning can be performed in two ways: authenticated (with system credentials) and unauthenticated.
Authenticated scans provide more in-depth results but require higher levels of access.
4. Reporting
Throughout the process, it’s important to document and report on identified vulnerabilities, remediation efforts, and overall progress. This reporting helps stakeholders understand the organization’s security posture and track improvements over time.
5. Remediation
Organizations must take steps to address identified vulnerabilities by patching systems, reconfiguring settings, or implementing additional security measures.
After completing remediation efforts, it’s crucial to verify that the vulnerabilities have been successfully addressed. This often involves re-scanning the affected systems to ensure that the weaknesses no longer exist.
Why businesses need vulnerability management
Vulnerability management helps businesses significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and other security incidents by regularly assessing systems for potential threats and addressing them quickly.
Also, vulnerability management is often a key requirement for compliance with industry regulations such as HIPAA or PCI DSS. These standards require organizations to regularly assess their systems for vulnerabilities and take steps to mitigate them.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provides comprehensive guidance on developing effective vulnerability management plans, emphasizing its importance in modern cybersecurity strategies.
Implementing a vulnerability management program
By following the next steps and maintaining a proactive approach to vulnerability management, businesses can significantly enhance their security posture and better protect themselves against evolving cyber threats.
- Develop a comprehensive asset inventory.
- Implement regular vulnerability scanning, including both automated and manual assessments.
- Establish a risk-based prioritization system for addressing vulnerabilities.
- Create clear processes for remediation, including patch management and configuration changes.
- Implement continuous monitoring to detect new vulnerabilities as they emerge.
- Regularly review and update the vulnerability management program to adapt to new threats and organizational changes.
- Provide training to staff on identifying and reporting potential vulnerabilities.
- Consider engaging with external cybersecurity experts for additional support and expertise.
Vulnerability databases and scoring systems
Organizations rely on standardized databases and scoring systems to manage vulnerabilities effectively. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) is a comprehensive repository of vulnerabilities maintained by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Through the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) list, each vulnerability in the NVD is assigned a unique identifier.
Types of vulnerabilities
Understanding the vulnerabilities that can affect an organization is crucial for effective management. Common examples include:
- Unpatched software: Software with known security flaws still needs updating. Learn the importance of system patching.
- Weak passwords: Easily guessable passwords that attackers can crack.
- Misconfigured settings: Improperly configured systems that leave security gaps.
- Outdated hardware or software: Legacy systems that may no longer receive security updates.
- Single-factor authentication: Reliance on passwords alone without additional verification methods.
- Poor firewall configurations: Improperly set up firewalls that don’t adequately protect the network.
- Phishing vulnerabilities: Susceptibility to social engineering attacks that trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Outdated antivirus and anti-malware solutions: Security software must be updated and may miss new threats.
How can your business detect potential vulnerabilities?
Effective vulnerability management doesn’t exist in isolation. Businesses should integrate different security processes and tools to create a comprehensive security strategy.
This integration may include:
- Patch management: Coordinating vulnerability identification with patch deployment to ensure timely remediation.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Incorporating vulnerability data into SIEM systems for better threat detection and response.
- Compliance monitoring: Aligning vulnerability management practices with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR.
- Penetration testing: Using vulnerability data to inform and guide penetration testing efforts.
Emerging trends in vulnerability management
Technology is an ever-evolving field, with novelties being introduced more frequently and some areas changing almost daily. The digital world is doubtless the fastest field to change. Unfortunately, that also includes threats evolving faster than the tools to prevent them.
Businesses need to take steps to protect themselves from these threats by implementing anticipatory preparation strategies such as strong password policies and multifactor authentication. They should also keep more than one updated backup, at least one on-site, and a remote backup. Additionally, businesses should regularly update their software applications and ensure that their firewalls are properly configured.
Cybersecurity companies and experts frequently develop and introduce new tools and technologies to keep up with cyber threats and enhance security.
- AI and machine learning: Advanced algorithms are used to predict vulnerabilities and prioritize risks more accurately.
- Cloud-based vulnerability management: As organizations move to the cloud, vulnerability management solutions adapt to scan and protect cloud-based assets.
- Automated remediation: Some advanced solutions now offer automated remediation capabilities for certain vulnerabilities, reducing the manual workload on IT teams.
- Continuous adaptive risk and trust assessment (CARTA): This approach advocates for real-time, context-aware vulnerability management that adapts to changing conditions.