Phobos ransomware is a type of cyber threat that infiltrates victims’ machines and encrypts the data in it. Then, it requests a payment in exchange for the description key. However, paying the ransom demand does not guarantee the actors will send the decryptor or that it will work.
In this in-depth article, we delve into the Phobos ransomware family, offering insights into its modus operandi and detailing the indicators of compromise (IOC) linked to the group’s activities.
Understanding the specific industries targeted by this ransomware and gaining insights into its operational methods are crucial for enhancing cybersecurity measures and fortifying defenses against ransomware attacks.
Phobos ransomware overview
Phobos ransomware is a cyber threat that has posed a risk to businesses and individuals alike since its emergence in 2018.
Sharing structural similarities with Crysis and Dharma ransomware, Phobos leverages a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model, making it accessible even to cybercriminals with limited technical expertise.
Operating primarily on Windows systems, Phobos exploits vulnerabilities in Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), either through phishing campaigns or direct exploitation of weak credentials or open ports. Once infiltrated, Phobos swiftly embeds itself into critical system locations, ensuring persistence through registry keys, and systematically encrypts user files and network shares using robust encryption algorithms like AES-256 and RSA-1024.
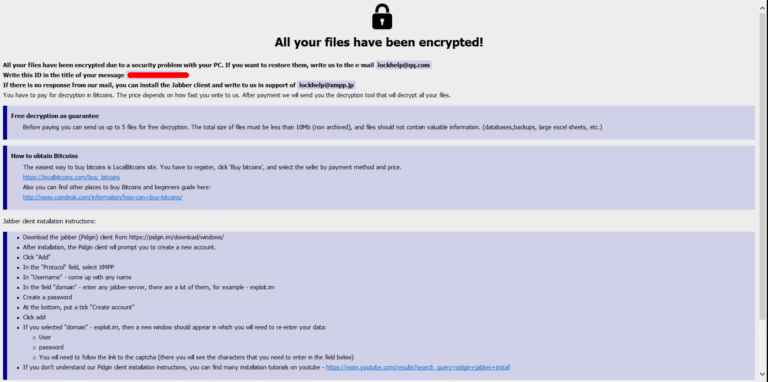
The aftermath of a Phobos ransomware attack leaves victims in a precarious position, with encrypted files renamed with distinct identifiers and a ransom demand typically communicated through an ominous ransom note.
Unfortunately, decryption tools for Phobos are not readily available, amplifying the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures such as regular backups, software updates, and the deployment of robust security protocols like firewalls and antivirus software.
How to identify Phobos ransomware: Main IOCs
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) are critical forensic clues that aid in recognizing malicious activity or malware linked to a cyber attack. They encompass encryption extensions, file hashes, IP addresses, and other pertinent details that cybercriminals leave behind during the infiltration of a machine or system.
Cyberthreat ID tools, such as the free ransomware ID tool by ProvenData, are also an effective and simple way to discover which variant infected your computer or network.
Note: Certain indicators necessitate a degree of technical expertise, such as hash files, potentially requiring the involvement of your IT team or a professional digital forensics service provider.
Phobos ransomware-specific IOCs include:
Phobos ransomware-specific IOCs include:
File Extensions. File names are usually changed to add the victim ID and the extension ‘.acute’.
Ransom Note. The note is embedded in the ransomware executable and they are displayed usually with the info.txt and info.hta names.
How to handle a Phobos ransomware attack
Dealing with a ransomware attack is complex and demands expertise. Therefore, it’s advisable to enlist the assistance of a trusted data recovery service to assist with data retrieval and ransomware removal from your system.
Pro tip: Reporting the attack to law enforcement bodies like the FBI and cybersecurity organizations aids in preventing future breaches and apprehending culprits.
We highly recommend reaching out to cybersecurity services for ransomware incident response. The less you change on your machine, the higher the chances of full data recovery are.
Preserve all evidence, like file encryption and the ransom note, so technicians can work using these details.
Proven Data technicians not only recover ransomware-encrypted data but also furnish comprehensive forensic reports and expedite incident response, mitigating business downtime and financial repercussions.
How Phobos ransomware works
Phobos ransomware operates through a series of steps, leveraging vulnerabilities and employing encryption techniques to compromise systems and extort victims.
Here’s a breakdown of how Phobos works:
1. Initial Access
Phobos gain entry into systems either through exploiting vulnerabilities in Remote Desktop Protocols (RDP) or via phishing campaigns.
2. Infiltration and Encryption
Once inside the network, Phobos begins its encryption process. It utilizes advanced encryption algorithms such as AES-256 and RSA-1024 to encrypt a wide range of files, including documents, media, and user-generated content.
3. File Modification and Ransom Note
After encryption, Phobos appends a unique file extension to the encrypted files. This extension typically contains an identification number, an email address for contacting the attackers, and an additional identifier.
Alongside the encrypted files, Phobos drops a ransom note, informing victims of the encryption and providing instructions on how to pay the ransom to obtain the decryption key.
Important: Do not pay the ransom. Paying the ransom does not guarantee that you will get your data back, and it may encourage the attackers to continue their criminal activities. Check our in-depth article on what happens if you pay the ransom.
4. Obfuscation and Persistence
Phobos takes steps to hinder recovery efforts and maintain persistence within the compromised systems. It deletes shadow copy backups, blocks recovery mode, and disables security measures like firewalls to evade detection and removal attempts by security software.
Phobos ransomware main targets
Industries dealing with sensitive or critical data are prime targets for Phobos. These include healthcare, finance, legal, and government sectors where data security is paramount.
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs) are particularly vulnerable to Phobos ransomware due to limited resources for cybersecurity measures.
Phobos ransomware indiscriminately targets business servers and networks, with a focus on SMBs, industries with critical data, and companies with weak security measures.
Phobos ransomware has a global reach, affecting businesses and organizations worldwide. Its global reach and ransomware-as-a-service model make it a persistent threat to organizations of all sizes and sectors.
How to prevent Phobos ransomware attacks
By implementing preventive measures and adopting a proactive approach to cybersecurity, organizations and individuals can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to Phobos ransomware attacks and other similar threats.
Consult cybersecurity professionals
Consult cybersecurity professionals
Cybersecurity consultation services can assist your business in increasing its defenses against cyber threats and ensure an immediate incident response.
Proven Data provides cybersecurity services designed to safeguard your data against malicious actors. Our offerings range from vulnerability assessments, ensuring your systems remain fortified against cyber threats, to Incident Response (IR) services, providing swift action in the event of an attack.
Additionally, we offer managed detection and response (MDR) services, empowering organizations to enhance their security stance, mitigate risks, and safeguard sensitive data and assets effectively.
Keep software updated
Regularly update operating systems, applications, and security software to patch known vulnerabilities. Phobos often exploits weaknesses in outdated software to gain access to systems.
Use strong passwords
Implement strong, unique passwords for all accounts and services, especially those connected to Remote Desktop Protocols (RDP). Avoid using default or easily guessable passwords, as Phobos commonly targets systems with weak credentials.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Enable MFA wherever possible to add an extra layer of security to accounts and systems. This can help prevent unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
Restrict remote desktop access
Limit Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) access to essential users and devices only. Consider using virtual private networks (VPNs) or implementing network-level authentication to enhance security.
Educate users
Train employees and users to recognize phishing attempts and avoid clicking on suspicious links or email attachments. Phobos often infiltrate systems through phishing campaigns, so raising awareness about email security is crucial.